Abstract
The Union Budget 2025 is a critical policy instrument shaping India’s economic trajectory and influencing capital markets. This paper examines the stock market’s response to key fiscal announcements, sectoral implications, and macroeconomic considerations. Utilizing a financial analysis framework, the study identifies ten key takeaways, including market sentiment, taxation policies, fiscal deficit management, and foreign investment flows. The findings highlight the interconnectedness between government policy and equity market performance, offering insights for investors and policymakers.
Introduction
The Union Budget serves as a strategic roadmap for economic development, impacting investor sentiment, corporate earnings, and financial market stability (Goyal, 2023). The stock market, as a barometer of economic confidence, reacts dynamically to budgetary provisions. This study assesses how fiscal measures in the Union Budget 2025 influenced major stock indices, sectoral performances, and institutional investment trends.
Methodology
The study employs an event-based analysis approach, drawing data from market reports, investor sentiment indices, and historical stock performance trends. Secondary sources, including policy documents and financial expert opinions, supplement the findings.

Key Takeaways
1. Market Sentiment and Index Volatility
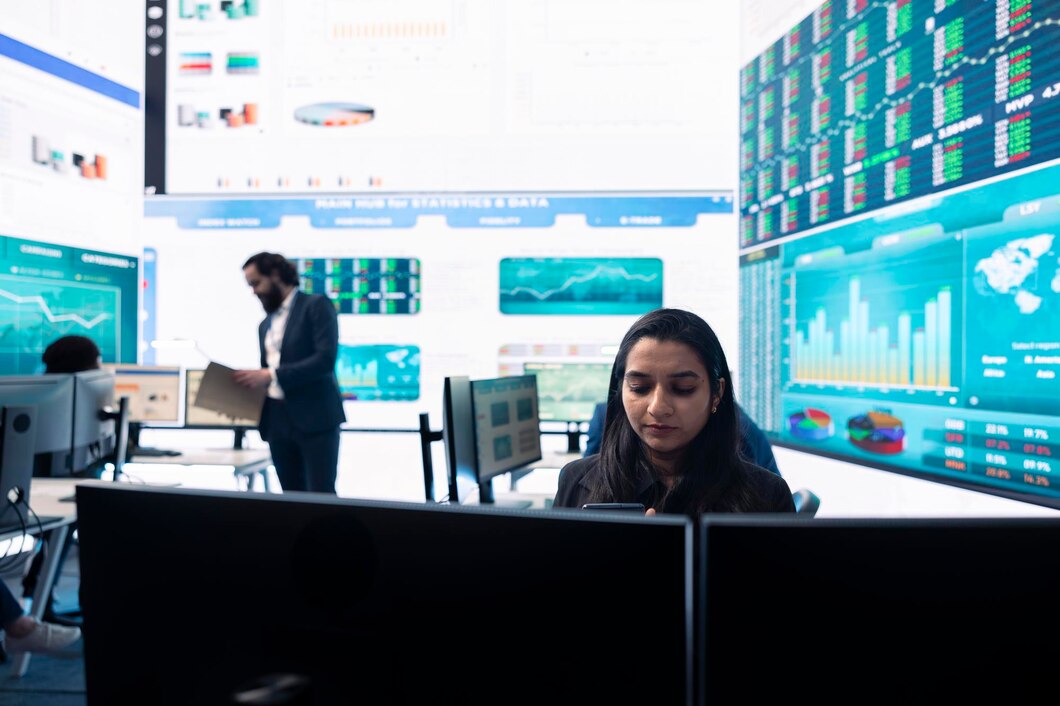
Stock indices such as the Nifty 50 and Sensex exhibited significant volatility post-budget, reflecting investor sentiment. The fluctuations were driven by factors such as fiscal deficit targets, sector-specific policy interventions, and global economic conditions (RBI, 2024). Initial reactions included heightened trading volumes, with market participants realigning their portfolios based on government priorities.
2. Fiscal Deficit and Bond Yield Implications
The fiscal deficit target for 2025 played a crucial role in shaping bond market trends. A lower-than-expected fiscal deficit led to a decline in bond yields, strengthening investor confidence in sovereign debt instruments (Economic Survey, 2024). A higher deficit, on the other hand, would have exerted inflationary pressures, potentially prompting the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to adopt a more hawkish monetary stance.
3. Taxation Policies and Market Adjustments
Changes in capital gains tax, securities transaction tax (STT), and corporate tax rates directly influenced stock market behavior. An increase in STT typically leads to reduced trading volumes, particularly in derivative markets (Bose, 2023). Conversely, tax incentives for long-term investors stimulate capital inflows into equity markets.
4. Sectoral Winners and Losers
Sectoral performance varied based on budget allocations and taxation policies. Key beneficiaries included:
Infrastructure and construction: Boosted by increased capital expenditure.
Renewable energy: Gained momentum due to green investment incentives.
Manufacturing: Benefited from production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes.
Conversely, sectors such as liquor, tobacco, and fossil fuel-based industries faced headwinds due to higher taxation and regulatory interventions (FICCI, 2024).
5. Disinvestment and Privatization Strategy
The government’s disinvestment roadmap played a crucial role in market expectations. Strategic sales of public sector undertakings (PSUs) and asset monetization plans were instrumental in driving investor confidence in PSU stocks. A well-defined privatization policy fosters capital market growth by improving public sector efficiency and attracting institutional investments (NITI Aayog, 2024).
6. Foreign Institutional Investment (FII) Trends
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) responded to fiscal measures, with capital flows influenced by tax policies, ease of doing business reforms, and geopolitical considerations. Favorable policies, such as relaxed foreign direct investment (FDI) norms, tend to attract FIIs, while excessive regulatory interventions can trigger capital outflows (IMF, 2024).
7. Infrastructure and Capital Expenditure (Capex) Allocation
Increased capex spending on highways, railways, and smart cities enhanced investor sentiment in capital-intensive sectors. This focus on public infrastructure development fosters long-term economic growth and positively impacts equity markets by improving corporate earnings in construction-related industries (Ministry of Finance, 2024).
8. MSME and Startup Ecosystem Development
The Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector is a critical pillar of the Indian economy. Budgetary provisions such as credit guarantees, tax exemptions, and digital compliance frameworks provided a favorable ecosystem for MSME growth. Given their sensitivity to liquidity conditions, such measures support mid-cap and small-cap stock performance (SIDBI, 2024).
9. Digital Finance and Fintech Regulatory Developments
Regulatory frameworks for fintech companies, digital lending, and cryptocurrency taxation influenced market dynamics. Pro-investment policies in the digital payment ecosystem and government-backed initiatives for fintech startups bolstered market optimism. However, restrictive policies on cryptocurrency transactions and offshore investments tempered speculative activity in digital assets (RBI, 2024).
10. Consumer Demand and Inflationary Impact
Budgetary policies affecting consumer disposable income had direct implications for sectors such as automobiles, FMCG, and retail. Announcements related to GST rationalization, subsidy schemes, and direct benefit transfers influenced household consumption trends, thereby impacting corporate earnings in consumer-facing industries (NCAER, 2024).
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2025 played a pivotal role in shaping stock market trends, with sectoral allocations, taxation policies, and fiscal deficit management emerging as key determinants. The stock market’s post-budget trajectory will depend on corporate earnings, global economic conditions, and monetary policy adjustments. Investors are advised to adopt a data-driven approach, incorporating fundamental analysis and macroeconomic indicators to navigate market uncertainties effectively.
Article by,
Pravinkumar Khairnar
Trainer, Trader and Financial Consultant
+91-9209031123
References
1. Bose, S. (2023). Impact of Securities Transaction Tax on Trading Volumes. Financial Journal of India, 18(2), 45-60.
2. Economic Survey (2024). Economic Outlook and Fiscal Management Report. Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
3. FICCI (2024). Sectoral Growth Projections: Post-Budget Analysis. Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry.
4. Goyal, A. (2023). Fiscal Policy and Stock Market Responses in Emerging Economies. Journal of Financial Policy Studies, 20(1), 33-48.
5. IMF (2024). Global Economic Outlook and Emerging Market Trends. International Monetary Fund.
6. Ministry of Finance (2024). Union Budget 2025: Policy Directions and Economic Impacts. Government of India.
7. NCAER (2024). Consumer Spending and Inflationary Trends in India. National Council of Applied Economic Research.
8. NITI Aayog (2024). Strategic Disinvestment and Privatization: India’s Roadmap. Government of India.
9. RBI (2024). Monetary Policy Report and Bond Yield Trends. Reserve Bank of India.
10. SIDBI (2024). Credit Access and Growth Trends in the MSME Sector. Small Industries Development Bank of India.


Leave a Reply